
Professional and compact Hot-Wire Anemometer for turbulence measurements and frequency analyses
A Hot-Wire Anemometer (HWA) is a very basic instrument for measurements of turbulence intensity of air flow and for its frequency analyses. A HWA detects velocities from analog electrical signals continuously outputted from the CTA feedback circuit. The Hot-Wire sensors are very tiny, a diameter of about a few microns, and therefore bring high thermal responsiveness. Those small sensors enable to capture information of the microstructure of the flow. By traversing the probe, velocity distribution can be also measured.
The Smart CTA is a professional but easy-to-use Hot-Wire Anemometer. In a compact design, two CTA units are integrated, which enable not only a one-dimensional probe but also a two-dimensional probes to use just with one main unit. The Smart CTA offers the frequency response up to 20 kHz, so for most applications it can be employed.
Operating EnvironmentPower Supply
| Measurement Specifications (Main Unit) | |
| Method | Constant Temperature Anemometry (CTA) |
|---|---|
| Bridge | |
| Channel Number | 2 |
| Bridge Ratio | 12:1 |
| Set Resistance (for probe) | 4.5 to 45 Ω |
| Current Supply to Probe | < 350 mA |
| Feedback Circuit | |
| Output Voltage Range | 0 to 10 V DC |
| Frequency Response | < 20 kHz |
| Temperature | 5 to 35 °C |
| Humidity | 20 to 90% RH |
| Voltage | AC100V / 120V / 220V / 240 V (set prior to delivery) |
| Frequency | 50 Hz / 60 Hz |
| Appearance | |
| Dimension | 320 mm x 88 mm x 280 mm |
| Weight | approx. 3.8 kg |
| Software | |
| Function | Probe Calibration, Measurement, Graph Indication, Realtime Monitoring |
| Created Files | Probe Calibration File Measurement File Statistical Calculation Result File (csv) |
| Analysis Data (Statistical Calculation Result File) |
Average velocity value, Standard deviation, Min. velocity value, Max. velocity value, Turbulent intensity |
| Supported Operating System | Windows 10/11 (64bit), Japanese / English |
Specifications subject to change without notice.
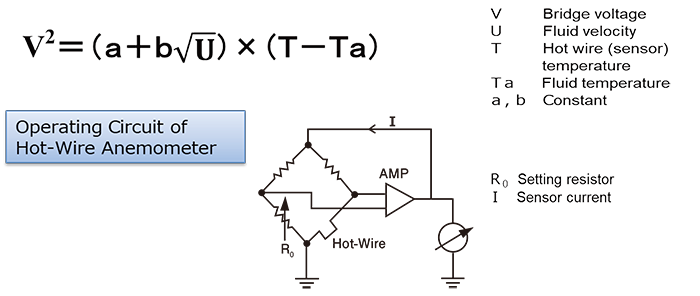
Hot wire anemometer uses the King’s equation.
It utilizes the phenomenon that the thermal energy dissipated from the heat rays (heated resistance wire) into the fluid depends on the fluid velocity.

Relation of the wind velocity and the amount of heat dissipation is known as the “King’s equation.”






Velocity in time-series and Histogram

Velocity in time-series and Power Spectrum